As fertility rate decreases and life expectancy increases, Korea is entering the super-aged society. Due to this demographic changes and COVID-19 pandemic, the need for a remote health-care system that can take care of the health and safety of elderly people living alone has been increasing. As health-care providers cannot manually monitor hundreds of screens, efficient and robust cloud-based services are in the spotlight. However, privacy concerns are a major obstacle because sensitive personal data is provided to cloud service providers. Thus, the preexisting home monitoring services for health care has been conducted only in limited areas.
Amidst this situation, a research team led by Professor Kim Mi-ran of the Department of Mathematics announced on August 31 that they developed a “security technology that can analyze human behavior without leakage of private information (hereafter “security technology”).” As such, Professor Kim is drawing attention from academia for the development of security technology that can expand the application of service by solving the security problems of preexisting home monitoring services for health care.
Develop international standards and new data security technology with homomorphic encryption

The security technology recently developed by Professor Kim’s team is a cloud-based security algorithm that can infer basic movements or behaviors, such as falling, with encrypted physical features information. Using this system, physical features information is encrypted and transmitted to the cloud, and behavior is inferred by the AI model to output the encrypted results for basic movement and falling. The resulting value is sent to the health-care service provider that can decrypt the code, allowing it to act immediately if risky activities such as falling are detected. This technology can provide reliable smart home monitoring services without privacy leakage, and it is expected to be adapted in various health-care service fields henceforth.
The core of this technology is homomorphic encryption, which is a cryptographic technology that can calculate encrypted data without decryption. This technology is expected to solve privacy issues that occur in every data industry as a next-generation cryptographic technology. In 2017, professor Kim developed an homomorphic encryption, the “Cheon-Kim-Kim-Song (CKKS) scheme,” which supports the computation of real numbers. The research paper has been attracting global attention with a total of 837 citations so far, being implemented by leading companies such as Microsoft Research and Intel, and being proposed as an international Standard Osganization (ISO).
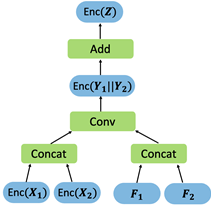
In this study, Professor Kim’s team mainly focused on designing a neural network model that can detect falling. They conducted a study to infer the Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) that analyzes action recognitions based on preexisting homomorphic encryption technology. The core of this technology is the high-speed computation technology with homomorphic encryption that can process the computation of parallel convolution in an encrypted state by saving single instruction in multiple data(SIMD).
The research team succeeded in improving the accuracy of the inference by designing a neural network optimized for homomorphic encryption. This not only enables the efficient analysis of large-capacity data but also optimizes the data storage space.
Professor Kim said, “Through joint research with Dr. Kristin Lauter (West Coast Head of Research Science at Meta AI Research) and Professor Xiaoqian Jiang (UTHealth), we succeeded in inferring AI models through the encryption of real visual data.” She added, “This technology can be used in various fields of cryptograph technology that is optimized to the Convolutional Neural Network algorithm in processing speed, storage area, and accuracy, which can be applied to various AI fields in the future.”
Expected to be used in healthcare and various AI fields with interdisciplinary research

Professor Kim, who is actively researching on the global stage of homomorphic cryptography and machine learning, is a new professor who started her research career in Hanyang University this semester. She said, “Big data analysis and artificial intelligence, the core technologies of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, can be used safely without information leakage with the homomorphic encryption.” She also added, “Various research was conducted to solve existing problems mathematically with theoretical designs of homomorphic encryption as well as apply them to various fields.”
Professor Kim is also actively conducting machine learning and outsourced genome analysis research. She also designed a “machine learning–based genotyping security algorithm” that can effectively replace missing values in genotyping data by fusing her two fields of research. In recognition of her active research achievements, she has been recognized for her research contributions, such as the “2018 Awards For Young Korean Female Mathematicians.”
She said, “Research on inference and prediction while protecting data privacy is conducted with machine learning models.” She added, “Developing a security technology that can analyze various genomes by encoding genomic information containing sensitive information is also in process.”
This study was conducted with the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) to support outstanding young scientists, and it was published in Nature Communications (IF 17.69), a multidisciplinary international journal, on the 15th.
Click to see the paper:


 '한양위키' 키워드 보기
'한양위키' 키워드 보기